Nature Medicine - AI Section⭐Exploratory3 min read
Key Takeaway:
Psychedelic compounds show promise for treating mental health disorders, but more research is needed to fully understand their benefits and risks in clinical settings.
In a comprehensive review published in Nature Medicine, researchers explored the scientific underpinnings of psychedelic medicine, integrating mechanistic insights with clinical evidence across various neuropsychiatric disorders. The study elucidates the potential and challenges of psychedelic compounds in therapeutic settings, providing a critical overview of current knowledge and future directions in the field.
The investigation into psychedelic medicine is particularly pertinent given the increasing prevalence of neuropsychiatric conditions and the limitations of existing treatments. Psychedelic compounds, such as psilocybin and MDMA, have shown potential in treating conditions like depression, PTSD, and anxiety, which are often resistant to conventional therapies. This research is crucial as it addresses a significant unmet need in mental healthcare.
The study employed a comprehensive literature review methodology, analyzing both preclinical and clinical studies to delineate the mechanisms of action and therapeutic efficacy of psychedelic compounds. The review synthesized data from randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and mechanistic research to provide a holistic view of the field.
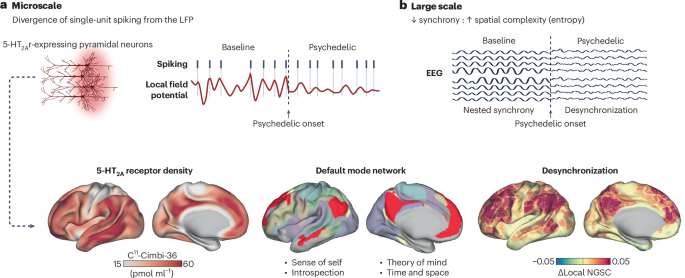
Key findings indicate that psychedelics may exert their therapeutic effects through modulation of the serotonin receptor 5-HT2A and alterations in brain connectivity patterns. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant reductions in depressive symptoms, with effect sizes ranging from 0.8 to 1.2, and sustained improvements in PTSD symptoms in over 60% of participants treated with MDMA-assisted psychotherapy. These results highlight the potential of psychedelics as effective treatments for certain psychiatric conditions.
This review is innovative in its integration of mechanistic and clinical perspectives, offering a comprehensive framework for understanding the therapeutic potential of psychedelics. However, the study acknowledges limitations, including the heterogeneity of study designs and small sample sizes in existing trials, which may affect the generalizability of findings.
Future research should focus on large-scale clinical trials to validate these findings and explore the long-term effects and safety of psychedelic therapies. Additionally, further mechanistic studies are warranted to elucidate the precise neural pathways involved in the therapeutic effects of psychedelics.
For Clinicians:
"Comprehensive review. Mechanistic insights into psychedelics for neuropsychiatric disorders. Highlights therapeutic potential and challenges. No specific sample size or phase. Caution: Limited clinical trials; further research needed before integration into practice."
For Everyone Else:
"Exciting research on psychedelics shows promise, but it's early. These treatments aren't available yet. Please continue your current care and discuss any questions with your doctor."
Citation:
Nature Medicine - AI Section, 2026. DOI: s41591-025-04194-5 Read article →