ArXiv - Quantitative BiologyExploratory3 min read
Key Takeaway:
Digital replicas of human organs could soon enable personalized treatment plans by accurately simulating individual health conditions and responses to therapies.
Researchers conducted a comprehensive review on the development of digital twins for various human organs, highlighting their potential to revolutionize personalized healthcare through enhanced simulation and prediction of individual physiological processes. This study is pivotal for advancing personalized medicine, as digital twins offer the possibility of tailoring medical treatment to the unique anatomical and physiological characteristics of individual patients, thereby improving outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
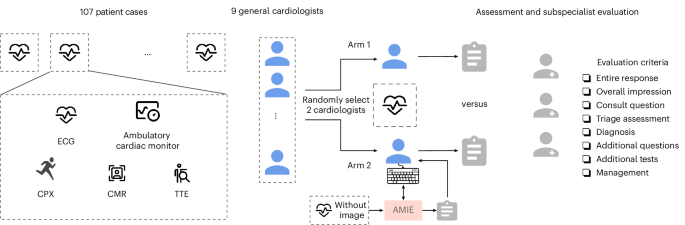
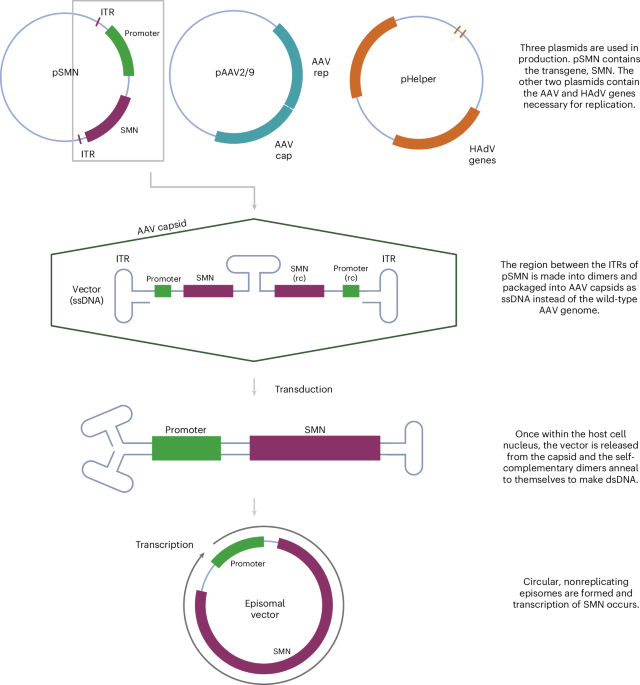
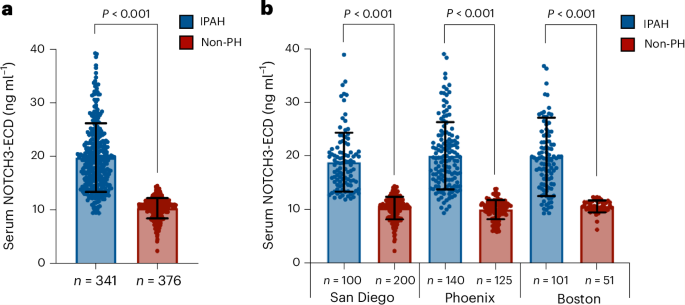
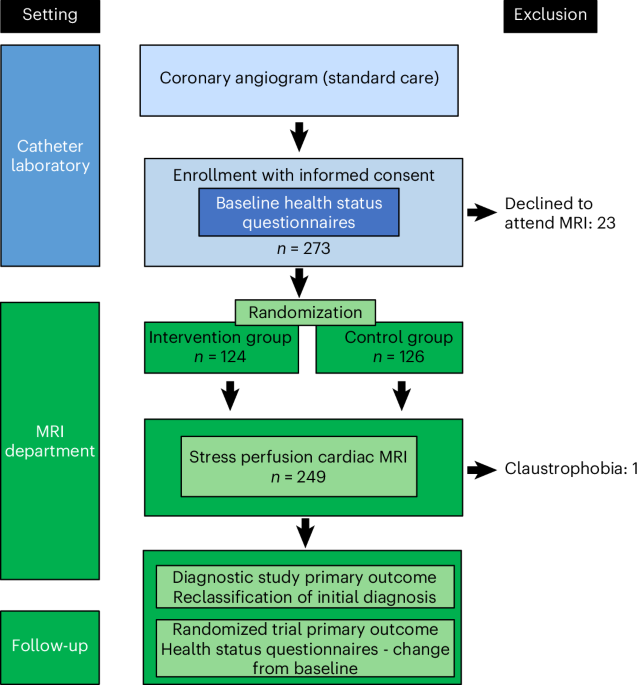
The research involved a systematic survey of existing methodologies utilized in the creation of digital twins, focusing on the challenges of anatomical variability, multi-scale biological processes, and the integration of multi-physics phenomena. The study meticulously analyzed different approaches, including computational modeling, machine learning algorithms, and data integration techniques, to construct accurate and functional digital replicas of human organs.
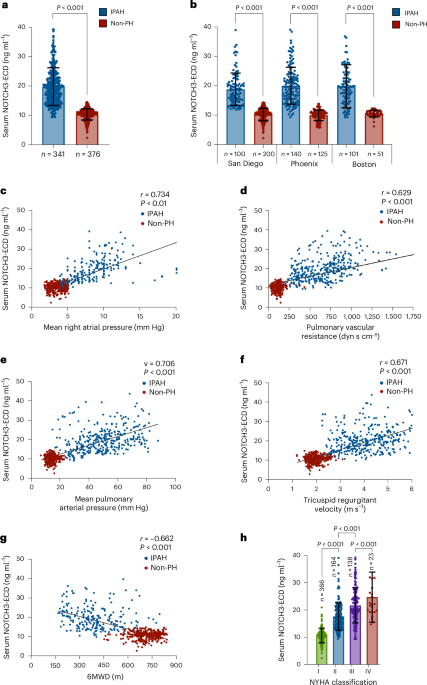
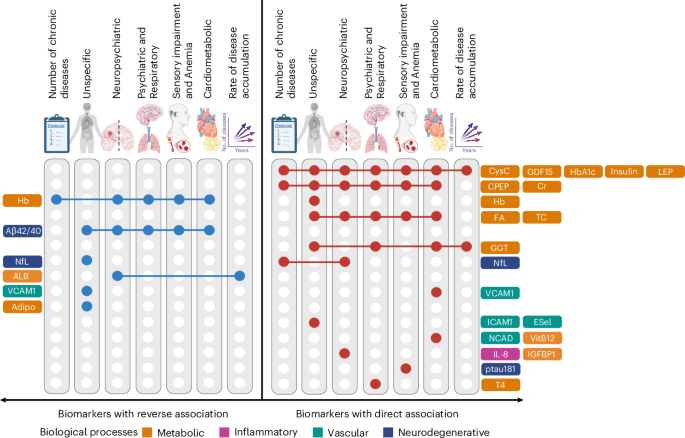
Key findings from the review indicate that while substantial progress has been made in the development of digital twins, significant challenges remain. For instance, the integration of diverse data types, such as genomic, proteomic, and clinical data, into a cohesive model is a complex task that requires sophisticated computational techniques. Additionally, the study emphasizes the importance of capturing the dynamic nature of physiological processes, which necessitates real-time data processing and continuous updating of the digital twin models.
The innovative aspect of this research lies in its comprehensive evaluation of multidisciplinary approaches to digital twin construction, highlighting the necessity for collaboration across fields such as bioinformatics, computational biology, and engineering. However, the study acknowledges several limitations, including the current lack of standardized protocols for model validation and the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security.
Future directions for this research include the validation of digital twin models through clinical trials and the development of standardized frameworks for their deployment in clinical settings. Such advancements are essential for realizing the full potential of digital twins in personalized healthcare, ultimately leading to more precise and effective medical interventions.
For Clinicians:
"Comprehensive review, no sample size. Highlights potential of digital twins in personalized care. Lacks empirical data and clinical trials. Await further validation before integration into practice. Monitor developments for future application."
For Everyone Else:
"Exciting research on digital twins for personalized care, but it's still early. It may take years before it's available. Continue following your doctor's advice and don't change your care based on this study."
Citation:
ArXiv, 2026. arXiv: 2601.11318 Read article →