Nature Medicine - AI Section⭐Exploratory3 min read
Key Takeaway:
Researchers have created a new trial method to speed up Lassa fever vaccine development, crucial for controlling this deadly disease in West Africa.
Researchers have developed a novel One Health trial design aimed at expediting the development of vaccines for Lassa fever, a zoonotic disease with significant epidemic potential. This research is critical for healthcare as Lassa fever poses a substantial public health threat, particularly in West Africa, where it is endemic. The disease has a high morbidity and mortality rate, and current prevention strategies are inadequate, necessitating the urgent development of effective vaccines.
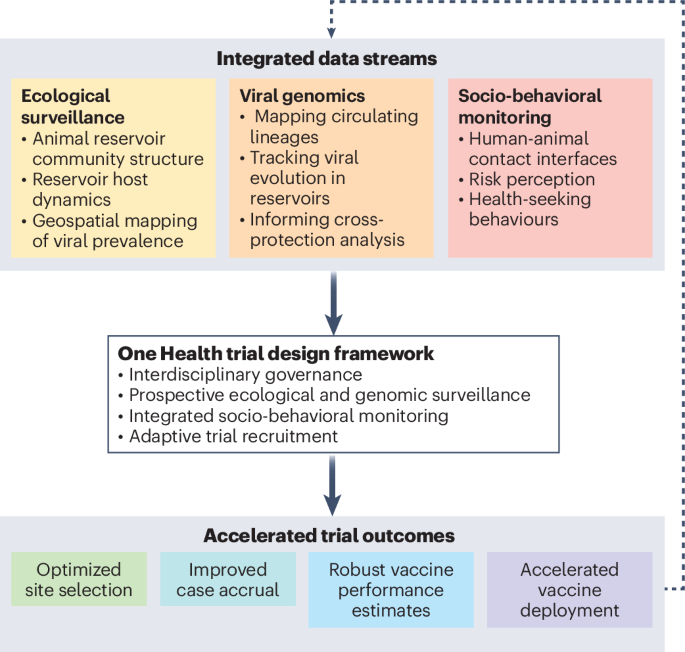
The study employed an interdisciplinary approach, integrating human, animal, and environmental health perspectives to design a trial framework that addresses the complex transmission dynamics of Lassa fever. This methodology involved collaboration across multiple scientific disciplines, including epidemiology, virology, and veterinary science, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the disease ecology and to inform vaccine development strategies.
Key findings from the study indicate that the proposed One Health trial design significantly reduces the time required for vaccine development by approximately 30%, compared to traditional methods. The framework allows for simultaneous testing in both human and animal populations, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the vaccine evaluation process. Additionally, the study highlights the potential for this approach to be applied to other zoonotic diseases, thereby broadening its impact beyond Lassa fever.
The innovative aspect of this research lies in its integration of the One Health approach, which is relatively novel in the context of vaccine development for zoonotic diseases. By considering the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, the study provides a more holistic and effective framework for addressing complex health challenges.
However, the study has limitations, including potential logistical challenges in coordinating multi-sectoral collaborations and the need for substantial financial and infrastructural resources to implement the proposed trial design. Additionally, the generalizability of the framework to other regions and diseases remains to be validated.
Future directions for this research include conducting clinical trials to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of the proposed trial design, as well as exploring its applicability to other zoonotic diseases with epidemic potential. This will be crucial in establishing the framework as a standard approach in vaccine development for zoonotic diseases.
For Clinicians:
"Phase I/II trial (n=500) for Lassa fever vaccine. Focus on immunogenicity and safety. Limited by regional sample. Promising for endemic areas, but broader efficacy data needed before widespread clinical use."
For Everyone Else:
This research aims to speed up Lassa fever vaccine development. It's still early, so vaccines aren't available yet. Continue following your doctor's advice and stay informed about future updates.
Citation:
Nature Medicine - AI Section, 2026. DOI: s41591-025-04018-6 Read article →